TL;DR
- Legacy web security tools (WAFs, endpoint detection) don’t see what happens inside the browser. This keeps client-side code execution as an unmonitored layer with hidden security risks.
- Client-side security tools have emerged to fill this gap and detect threats including Magecart, data exfiltration, and manipulation of browser elements.
- Purpose-built client side security tools include cside, Feroot, and Jscrambler.
- Solution evaluation should take into account: protection depth, ease of implementation, and pricing (which many vendors keep hidden behind sales calls, resulting in wildly different estimates for similar functionality)
Comparison Table: Client-side Security Tools
Most large web security vendors market a “client-side security” or “page protection” feature, but these are often limited in capability and exist to be a sales add-on.
Below is a curated list of companies that are genuinely advancing this space and tackling the obscurity of browser-layer visibility.
| cside | Feroot | Jscrambler | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protection Approaches |
Multiple, configurable layers:
|
|
|
| Pricing |
|
|
|
| Ease of Implementation |
|
|
|
| Reviews | 4.9/5 on Sourceforge | 4.9/5 on G2 | 4.5/5 on Sourceforge |
| AI-Driven Security Analysis & Compliance Documentation | Yes | Yes | Limited |
| Protects Against |
|
|
|
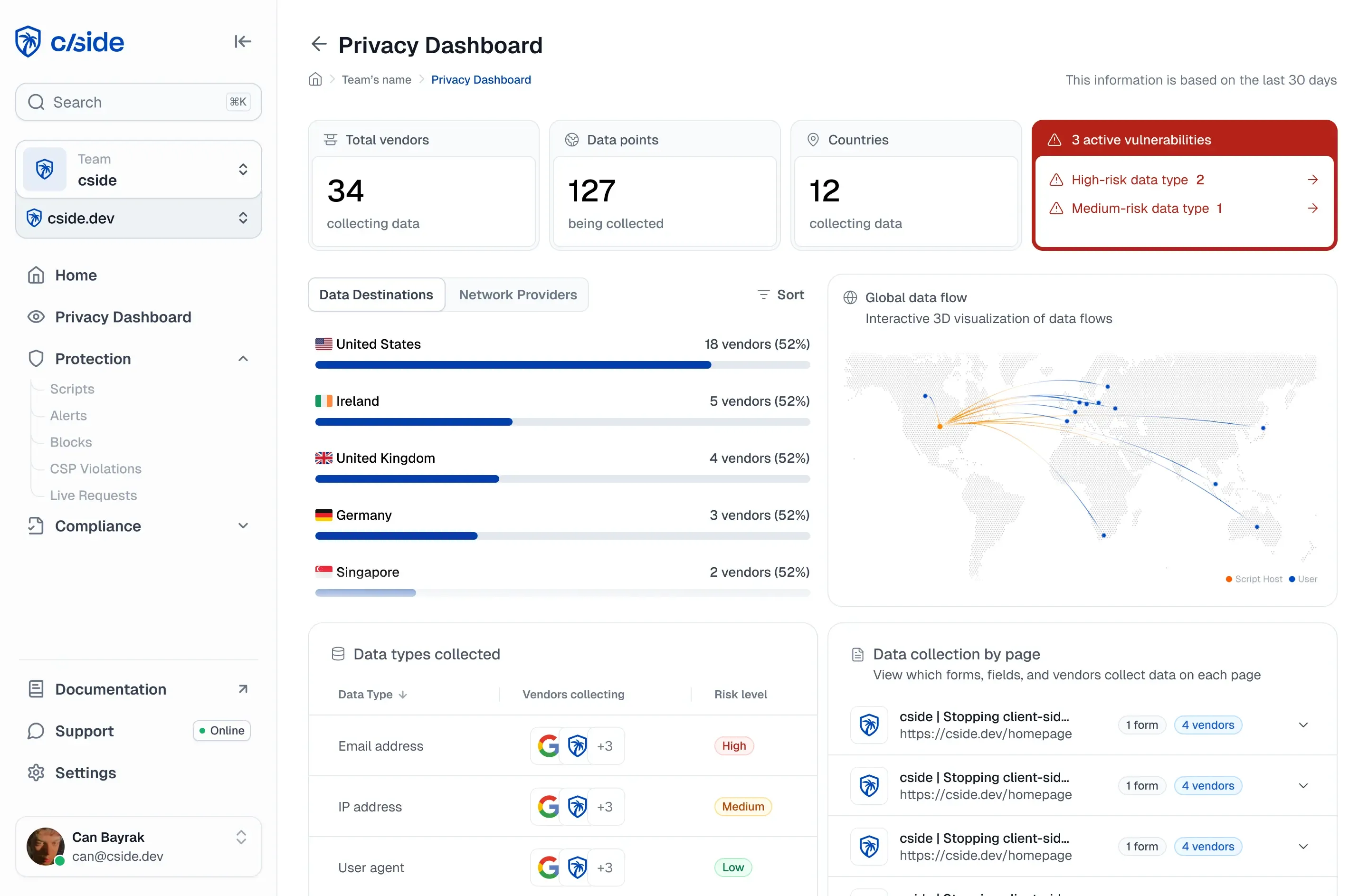
Why Client-side Security Matters

Websites and web applications contain a mix of code - most written internally, and some code pulled in from third parties. Think of third party scripts like chatbots, analytics tools, and accessibility libraries. Every single one of these introduces security risks to your website. These scripts are typically approved once, frequently changed, and rarely reviewed. That’s why attackers love this surface as an entry point. For example, once an attacker gains access to Google Tag Manager, they can inject code that makes it straight to the live website.
What is client-side security:
- Client-side security
- Client-side security protects everything executed in a user’s browser, including front-end code, JavaScript, CSS stylesheets, and third-party scripts. These browser-loaded elements can be abused to steal data, redirect users, or run fraud. Client-side security solutions monitor and, in some cases, block suspicious browser-layer behavior to protect web visitors.
Who needs client-side security
Sensitive data is increasingly processed in the browser, making client-side visibility a company wide necessity.
- Security teams: Detecting client-side threats like script injections, data exfiltration, and malicious code that exists outside of the server & AppSec perimeter.
- Privacy & compliance teams: Demonstrating safety controls for frameworks like PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA/CPRA, HIPAA and more.
- E-commerce teams: Maintaining checkout integrity by detecting modified scripts (Magecart) before they steal user payment data.
- Fraud teams: Catching signs of fraud earlier with client-side signals including chargeback abuse, malicious AI agents, and card testing bots.
Public research on the rise of client-side attacks
- cside detects 72,000 compromised websites in Q2 2025
- Client-side attacks detected by Insikt Group climbs by 3x in 2024 compared to 2023
Comparison of the Best Client-side Security Tools (Features, Reviews)
1. cside Client-side Security
cside was founded by veteran security engineers that noticed the client-side visibility gap in web security. As a pioneer in bringing AI into client-side protection, cside has won multiple industry awards for their unique multi-layer approach.
cside regularly publishes client-side security research and contributes to bodies like the W3C. Their engineers regularly speak at industry events to educate business leaders on modern web attacks. Alongside client-side security, the cside platform suite includes AI agent detection, payment fraud detection, and website privacy compliance automation.

Security features
- Detection of client-side attacks such as formjacking, magecart, and data exfiltration. Covers first, third, and fourth party scripts.
- Script payload & runtime analysis to identify signs of malicious JavaScript behavior (keylogging, iframe injections, suspicious redirects, DOM manipulation)
- Advanced protection on payment pages against credit card e-skimming
- Automatic tracking of third-party scripts. Get alerted of suspicious signals when new scripts are added or existing script code changes.
- AI-enhanced review engine to reduce manual security assessments
- Threat feed to identify JavaScript supply chain exposures. If a vendor tool on your website (chatbot, analytics tool) is compromised you can take action before you are impacted.
- Integrates with SIEMs and existing security tools.

Compliance features
- AI-assisted script reviews, justifications, and mapping to legal categories
- AI-assisted documentation prep for PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA/CPRA, and more compliance frameworks
- Forensic history of scripts for incident investigations
- Proof of security safeguards against client-side attacks to satisfy requirements under PCI DSS, GDPR, CPRA, and more
- QSA validated solution for PCI DSS 4.0.1 requirements 6.4.3 & 11.6.1

Protection approach used
Multi-layer, configurable approach so that organizations can select appropriate measures based on data risk.
- Scanners
- Client-side agents (JS agents) for runtime analysis
- AI-enhanced script risk analysis
Pricing
- cside starts at $99/month (or $999 a year) and you can get an immediate estimate on the pricing page.
- cside pricing is based on website pageviews to protected pages.
- cside covers unlimited domains and pages, even on the base plan.
- A free forever plan is available for users to tour the platform, set up basic protection, and upgrade any time for full coverage.
Reviews
cside is highly rated across public review platforms:
| Reviews | Rating |
|---|---|
| cside reviews on SourceForge | 4.9 / 5 stars |
| cside reviews on G2 | 4.8 / 5 stars |
“The detection capabilities we got with cside were unlike anything we saw in other products we tested in the past. We would definitely recommend the product for PCI and more.” - Mark D.,
(Quote from G2 Review of cside)
Ease of implementation
cside offers multiple deployment options, allowing teams to balance security depth with ease of implementation. The cside script takes a few minutes to add to your site and will instantly collect data and protect your pages. For larger enterprises, setting up deployment with help from a guided support typically takes days to weeks.
cside allows users to set up protection through a fully self-service model. This makes it easy for organizations to tour the platform before initiating a sales process, or fully deploying on their own for a rapid set up.
Pros
- Flexible deployment options that adapt to different security and operational needs
- Cost-effective compared to traditional enterprise client-side tools (starting at $999 a year)
- QSA validated to pass PCI DSS 4.0.1 requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1
- Differentiated gatekeeper layer for deeper client-side visibility and control
- Self service option for small teams that don’t require hands-on support
- Client-side product suite includes website privacy compliance, AI agent detection, and fingerprinting offerings
2. Feroot
Feroot is a client-side security platform that analyzes how third-party and first-party JavaScript behave in the browser at runtime. The product surfaces risks related to client-side script execution, data flows, and unauthorized behavior.
Security features:
- Monitoring of third-party script and data flows to identify unexpected or high-risk behaviors in the browser.
- Real-time detection of malicious or unauthorized script activity, including dynamic injections and behavior changes.
- Automated visibility into script composition and software bill of materials (SBOM) to understand what is running on your pages.
- Support for compliance-oriented monitoring such as tracking script changes and logging behavior against PCI DSS requirements.
- Script classification and audit reporting to help document data access and third-party exposure.
Protection approach used
- Scanners
- Client-side agents (JS agents) for runtime analysis
- AI-enhanced script risk analysis
Pricing
- Feroot pricing is not listed publicly. They use a custom pricing model that requires a scheduled call for an estimate.
- Feroot does not offer a free trial or free plan.
Reviews
Feroot is well rated across public review platforms:
| Reviews | Rating |
|---|---|
| Feroot reviews on G2 | 4.9 / 5 stars |
Ease of Implementation
Feroot uses monitoring-first deployment that involves adding a script to your web pages. As of the writing of this article, implementation requires scheduling a demo first and there is no free plan or self-service option for Feroot.
Pros
- Visibility into client-side scripts and data flows, including third-party and dynamically injected code.
- Real-time detection of unauthorized or risky behaviors that might indicate malware or supply-chain compromise.
- Support for compliance specific reporting requirements across GDPR, HIPAA, and other frameworks.
- Automated classification and reporting that can support audit evidence and risk reviews.
- Monitoring-first approach that reduces disruption to production environments and existing third-party dependencies.
3. Jscrambler
Jscrambler is a client-side protection and compliance platform. This vendor combines JavaScript obfuscation with runtime defenses and third-party script control. At its core, the solution helps organizations protect browser-side code from tampering and data leakage. The platform also offers capabilities for first-party code hardening.
Security Features
- First-party JavaScript obfuscation and hardening Jscrambler applies polymorphic code obfuscation to make it more difficult for attackers to reverse-engineer or tamper with application logic.
- Third-party tag control and visibility: The platform enables teams to manage how external scripts behave on their pages.
- Runtime behavior analysis: Jscrambler’s protections include the ability to detect and respond to unauthorized code modifications and anomalous client-side activity.
- Compliance monitoring: Built-in capabilities help meet PCI DSS v4 requirements by automating script integrity validation and monitoring.
- Multi-module protection: Separate modules such as Code Integrity and Webpage Integrity enable both deep code defense and broader page-level script protection.
Protection approach used
- Scanners
- Client-side agents (JS agents) for runtime analysis
- AI-enhanced script risk analysis
Pricing
- Jscrambler pricing is not listed publicly. All pricing estimates require a scheduled call.
- Jscrambler does not offer a free trial or free plan.
- Jscrambler charges per website / domain, which can add unexpected costs for enterprise websites with staging domains or multi-region domains.
Reviews
Jscrambler has mixed reviews across public review platforms:
| Reviews | Rating |
|---|---|
| Jscrambler reviews on SourceForge | 4.5 / 5 stars |
| Jscrambler reviews on G2 | 4.4 / 5 stars |
Ease of Implementation
Jscrambler aims for deployment with minimal impact on user experience. Depending on the modules chosen (Code Integrity, Webpage Integrity), teams can adjust the level of protection they apply.
Jscrambler does not offer a self service deployment and a formal sales process is required to gain access to the platform.
Pros
- Comprehensive client-side protection: Combines obfuscation with runtime defenses and third-party tag control in a unified platform.
- Supports compliance: Built-in mechanisms to help automate PCI DSS v4 script integrity and monitoring requirements.
- Real-time defenses: Detects and can respond to unauthorized code changes at runtime.
- Flexible protection modules: Separate modules for code obfuscation and page-level integrity give teams options in how they deploy.
- Trusted by enterprise users: Cited use across sectors that need to protect client-side logic, data flows, and compliance.
4. Reflectiz
Reflectiz is a web exposure and client-side risk management platform. Their solution monitors first, third, and fourth party code running on a website. Reflectiz uses a remote monitoring model (sometimes referred to as an “agentless” solution) that examines script behavior, tags, pixels, and iframes from an outside scan.
Security Features
- Continuous remote monitoring of website components
- Synthetic crawler that simulates user interactions to tracks script execution and network requests.
- Exposure risk rating and prioritization to help teams understand which exposures are highest risk.
- Real-time alerts and issue tracking to focus attention on meaningful code changes.
- Comprehensive inventory and dependency mapping that catalogs all web components and their interactions across the digital supply chain.
Protection approach used
- Scanners
- AI-enhanced script risk analysis
Pricing
- Reflectiz pricing is not listed on their website, however their Sourceforge listing mentions a starting price of $5,000/year.
- Reflectiz does not offer a free trial or free plan.
- Reflectiz charges per website, which can bring heightened costs for enterprises with staging domains or multi-region domains.
Reviews
Reflectiz ratings across public review platforms:
| Reviews | Rating |
|---|---|
| Reflectiz reviews on SourceForge | 4.7 / 5 stars |
Ease of Implementation
Reflectiz operates remotely and does not require installing a script on the monitored website. Most other vendors also offer this remote-only option, but it comes with limitations as it relies only on externally available data and can easily be evaded by attackers.
Pros
- Holistic web exposure monitoring across first, third, and nth-party components without adding code to production.
- Simulates user interactions and can highlight risky or anomalous script behavior.
- Inventory and baseline establishment to give teams a clearer understanding of their attack surface.
- Agentless deployment model that avoids site performance impacts
Legacy Web Security Tools Don't Monitor the Client-side
Web security has been around for decades. Unfortunately the focus has stayed on protecting servers, APIs, and networks. All valid attack surfaces. But this has left the browser layer as an obscure black box.
- WAFs: Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) filter inbound and outbound traffic between users and the application server. They’re effective but they stop at the network edge. Once the page loads in a user’s browser, the WAF has no visibility into what scripts execute, what data they access, or how they might change at runtime.
- Remote scanners: External scanners crawl websites from the outside. This is great for getting a quick snapshot. However, this approach misses true runtime behavior and is evaded by scripts that load conditionally.
“Traditional security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems are limited by their perspective of application and infrastructure runtime states from a provider’s point of view … these tools may overlook unintentional data leaks between client browsers and third-party services, as well as Magecart attacks that could exploit these trusted third-party services.”
ISACA Report, Traditional Security Solutions Fall Short in Protecting Against Web Client Runtime Risk, Sergei Vasilevsky and Kamal Govindaswamy
Approaches to Client-side Security
Several widely used approaches exist to add client-side security to your website. Each comes with different levels of visibility, protection, and ease of implementation. Ultimately it is recommended to layer different approaches together as each method observes a different part of the problem.
1. CSP and SRI

CSP
Content Security Policy is a browser mechanism that allows site owners (usually web developers) to define a list of external domains that are authorized to load scripts and other resources. This limits access to “trusted” sources.
CSP Limitations:
- CSPs require manual maintenance, which becomes difficult on modern sites with dozens of scripts that change frequently
- If a “trusted” vendor is compromised, code injections can pass right through CSPs without being detected.
SRI
Subresource Integrity (SRI) uses cryptographic hashes to verify that external resources haven’t been modified since deployment. This is another control mechanism that can be implemented by web developers on a site.
SRI Limitations:
- Subresource Integrity is effective for static, version-controlled scripts, but it breaks down with dynamic scripts. Most modern websites rely on dynamic scripts.
2. Remote Scanners

Remote scanners or “agentless” solutions crawl a website from the outside. They can inventory scripts, detect newly added resources, and flag differences that might suggest malicious changes. These solutions are the easiest to implement since they operate externally.
Limitations of scanners:
- This approach is evaded by scripts that load conditionally or mutate after execution.
- Independent research published on ISACA concludes that scanners provide a basic, limited view into client-side monitoring
3. Client-side Agents

Client-side agents work by adding a JavaScript tag onto a protected website. Script execution, data flows, and user interactions are continuously monitored. Unlike remote scanners these tools observe real runtime behavior that occurs on user browser sessions.
Limitations of Client-side Agents
- Since client-side agents are visible in browser code, attackers can see their presence and carry out sophisticated attacks to avoid them.
4. Multi-layer Approach with AI Analysis
cside combines remote scanning, client-side monitoring, and AI-enhanced detection to give teams deep visibility into browser activity. Policy controls can be informed by script behaviors instead of script source alone. Teams can allow approved scripts (that are behaving as expected) to access sensitive data. Other unauthorized scripts or trusted code that is suspiciously changed can be blocked. Each of these layers feeds into a centralized dashboard that connects to the rest of your environment (like CSPs and SIEMs).
Limitations of a multi-layer approach
- A multi-layer requires additional configuration before reaching full coverage. Most teams can still deploy this approach within days or weeks.
What client-side security protect against:
cside CEO Simon Wijckmans speaking on client-side security at PCI DSS industry event
Client-side security tools watch happens inside the user’s browser after the page loads. It protects against attacks that manipulate browser elements or inject code served to users:
- Malicious or injected JavaScript from compromised vendors or supply chain attacks
- Data exfiltration through hidden form captures or outbound network calls
- Checkout and form manipulation such as Magecart or formjacking
- Unauthorized script changes or new scripts introduced through tag managers
Client-side intelligence tools like cside add visibility that patches gaps in other fraud/website monitoring software:
- Privacy violations from unauthorized scripts collecting personal data beyond intended scope
- Signals of chargeback abuse or card testing bots
- VPN detection to adhere with age verification laws
- Governance controls for AI agents, allowing commercial agents to purchase while blocking malicious AI agents.
Client-side security with cside
As a pioneer in bringing AI into client-side protection, cside is on a mission to solve obscurity in web security that has blocked security teams for decades.
cside’s client side security solution helps organizations:
- Comply with PCI DSS 4.0.1 requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1
- Demonstrate client-side data protection controls for GDPR, CCPA/CPRA, and HIPAA.
- Protect payment pages from Magecart, formjacking, and other JavaScript-based data skimming attacks.
- Prevent exposure of sensitive user data from misconfigured or malicious third-party scripts
- Govern AI agents operating in the browser
You can start with our free plan or book a demo to see how client-side security supports your defense stack.